Module 9: Decentralized Lending and Borrowing
There is a lot to learn about decentralized lending and borrowing. Module 9 breaks down the different DeFi protocols for credit and loans. We will also explore how to earn interest and borrow on AAVE.
Introduction
In the previous module we examined decentralized exchanges, and in this module we will go deeper into decentralized lending and borrowing.
The lending and borrowing of crypto-assets is the most significant industry for decentralized applications (dapps) in today's data-centric world. Anyone with a compatible wallet can share and borrow cryptocurrencies using Dapp platforms. Because of this, DeFi lending platforms have become the latest financial service provider that sets itself apart from other financial institutions by providing the same security and confidence that is expected from blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
DeFi lending is a distributed and decentralized application system that allows investors and lenders to lend or deposit fiat for interest. This is an appealing alternative for lenders because it will enable them to earn a low-risk interest rate on their existing assets without sharing their data with third-party services.
Decentralized lending systems have become even more critical and inventive in recent years. The capacity to lend and borrow assets through entirely open applications has brought a significant milestone for banking and cryptocurrency.
There are no lending constraints in the DeFi world as the usual banking rules do not apply in this space. Anyone can receive capital if they have adequate collateral. Lending is no longer a privilege reserved for the wealthy. Borrowers can withdraw funds and return them at an algorithmically determined interest rate by contributing to a decentralized liquidity pool. Unlike applying for a loan at a bank, where strict client identification (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) regulations apply, DeFi requires only collateral to borrow.
DeFi Protocols for Credit and Loan Transactions
Next, we will explore how unbanked credit and loan mechanisms are possible with Aave and Compound Finance, the two leading DeFi protocols for credit and loan transactions.
Aave
Aave is a decentralized, non-custodial liquidity market platform in which users can participate as depositors or borrowers. According to the Aave website, "Depositors provide liquidity to the market to earn passive income, while borrowers can borrow over or under-collateralized loans."
If you want to use the Aave protocol, you first deposit the asset and amount you want. Shortly after, a lender earns passive income based on the demand for loans in the market. By depositing assets, consumers also have the option of borrowing by using the deposited assets as collateral. The interest you earn by depositing funds can help offset the interest rate users accumulate by borrowing.
The protocol itself uses a decentralized autonomous organization (or DAO). That means it's operated and governed by the people who hold—and vote with—AAVE tokens.
On Aave, there are eight key features:
Wide Range of Assets
Aave currently has 24 assets available for lending and borrowing as of April 2021. Aave has a history of quickly expanding its platform with new assets.
Stable and Variable Interest Rates on Loans
Borrowers have the option of selecting between fixed and variable interest rates.
Switching Rates
Borrowers have the option of choosing between fixed and variable interest rates.
Collateral Swap
Borrowers have the option of exchanging their collateral for another asset. This reduces the risk of loans falling below the required collateral ratio and having to be liquidated.
Repayment with Collateral
Borrowers can pay off their loan balances in one transaction by paying with their collateral.
Flash Loans
Borrowers can borrow without putting up any collateral if they repay the loan, as well as all additional interest and flash loan costs, in one transaction. Arbitrage traders benefit from flash loans because they are capital-efficient for arbitraging trades amongst DeFi Dapps.
Flash Liquidations
Liquidators can use Flash Loans to borrow funds as part of their liquidation bond while still receiving the liquidation bonus.
Native Loan Delegation
Borrowers can extend their credit line to other users who want to borrow at a higher interest rate without putting up any collateral.
How Liquidity Pools Work on Aave
In the early days of decentralized finance, if you wanted to borrow an asset, you had to find someone on the platform willing to lend it to you - at a price and on terms you both agreed upon. Aave skips the whole peer-to-peer lending process, opting instead for a kind of pool-to-peer lending.
Users deposit digital assets into "liquidity pools." These become funds that the protocol can then lend out. Everyone who deposits their tokens into a pool, "providing liquidity," receives new aTokens. (The "a" stands for "Aave.") So if you deposit DAI into the liquidity pool, you get aDAI in return.
As an aToken holder, you get a share of the platform's flash credits as well as interest on those aTokens. So if you deposit tokens into a pool that already has a lot of excess liquidity, you will not earn much. However, if you deposit tokens that the protocol desperately needs, you will earn more. The same goes for borrowers - interest rates vary depending on what you borrow.
How to Earn Interest on Aave
It's quite straightforward to earn interest on Aave: first, you must contribute assets to the Aave protocol.
You will receive a prorated amount of aTokens equal to your underlying asset after depositing your asset. For example, you will receive a USDT if you provide USDT. You will receive aYFI if you deposit YFI, and so on.
On each Ethereum block, interest on your aTokens accrues immediately. However, you will not receive your interest right away; you must redeem your aTokens to collect your principal as well as any accumulated interest.
How to Borrow on Aave
You must deposit an asset as collateral for the loan before you can borrow, and the amount deposited must be more than the amount borrowed. Aave uses a predetermined loan-to-value (LTV) ratio to decide how much a user can borrow. Each asset has a particular LTV, which can range from 15% to 80%.
Liquidators can liquidate up to 50% of your position if the LTV surpasses the asset's liquidation threshold, with an extra liquidation penalty of up to 15%, depending on the asset.
Please keep in mind that not all assets are eligible for use as collateral.
Compound Finance
Compound is a liquidity pool that runs on the Ethereum blockchain. Borrowers borrow from the liquidity pool and pay interest on their loan, while providers provide assets to the liquidity pool and receive interest on them. Thus, Compound effectively bridges the gap between lenders seeking interest on idle funds and borrowers seeking to lend funds for productive or investment purposes.
Interest rates at Compound are presented in Annual Percentage Yield (APY), and they vary depending on the investment. Compound interest rates are calculated using algorithms that include asset supply and demand.
Compound reduces lending/borrowing friction by allowing suppliers/borrowers to engage directly with the interest rate protocol without discussing loan terms (e.g., maturity, interest rate, counterparty, collaterals), resulting in a more efficient money market.
Compound is also more beginner-friendly compared to Aave as it has fewer features.
How to Earn Interest with Compound Finance
To receive interest, you must provide assets to the protocol. Compound accepts nine types of tokens. Once you deposit your funds into Compound, you immediately begin earning interest on your deposits. Interest is added to the deposited amount and calculated after each Ethereum block.
When you deposit, you will receive a corresponding amount of cTokens. For example, if you deposit DAI, you will receive cDAI; if you deposit Ether, you will receive cETH, and so on. The interest is not distributed immediately but accrues on the cTokens and can be exchanged for the underlying asset and the interest it represents.
Note: USDT is the only asset that cannot be used as collateral due to counterparty risk. Users must trust that each USDT is fully backed 1:1 by USD and that the reserve exists. Fear that an infinite amount of USDT could be minted to withdraw assets from the protocol.
What are cTokens?
cTokens are a back-end unit of account for the protocol. When a user provides cryptocurrency to the protocol, cTokens are used to manage the funds borrowed and the interest earned.
Each time a user provides funds to the lending pool, they are issued a corresponding balance of cTokens. This balance of cTokens is directly proportional to his share in the Lending Pool, which accrues interest with each block. Each asset has its own cToken. For example, when a user lends DAI to the protocol, they receive a corresponding credit of cDAI.
cTokens are ERC20 tokens, which means they can be viewed on Etherscan at any time and can also be stored in Ethereum wallets like the Coinbase wallet or Metamask. Etherscan is a tool that allows you to view data on pending or confirmed Ethereum blockchain transactions. On the website, you can browse transactions, blocks, wallet addresses, smart contracts, and other on-chain data.
cTokens can also be exchanged outside of the Compound protocol, just like all other ERC20 tokens. However, it is essential to note that users exchange their cTokens and exchange their corresponding share of the loan pool.
How to get a Cryptocurrency Loan Instantly Using Compound Finance
There are a few essential prerequisites to receive a crypto loan quickly utilizing the Compound crypto lending platform:
Compound-supported crypto assets (BTC, ETH, USDC, DAI, COMP, BAT, ZRX)
Compound-supported crypto wallet (MetaMask, Ledger, Trezor)
ETH in your crypto wallet to cover transaction costs (gas fees)
Once you have been set up with the above requirements, you need to decide how much you want to borrow. Remember that cryptocurrency prices are volatile unless you plan to use stablecoins like USDC as collateral. So, if you deposit ETH worth $10,000, a drop in the price of ETH could result in your ETH being worth $7,000 just a few days later. Therefore, it is essential to choose a low LTV ratio to account for price fluctuations. A safe LTV ratio usually starts at the 50% mark, but a recommended starting point is closer to 20% to 30%.
For crypto loans, a low LTV ratio means less stress, less maintenance, and better insulation from market fluctuations. Unfortunately, it also means you may have to put up more collateral than expected, depending on how much you want to borrow. However, this is ultimately a good thing as you are forced to hold on to your crypto assets through thick and thin while getting a low-risk crypto loan.
How to get Instant Crypto Credit through the Compound Protocol
Visit Compound and then click on the app then;
1. Connect your wallet.
2. Select the cryptocurrency you want to deposit and enter the amount. Click Deploy.
3. Sign two transactions (one to let Compound spend your cryptocurrency, the other to deposit it).
4. Select the cryptocurrency you want to borrow and enter the amount. Click borrow.
5. Sign two transactions (one to interact with Compound SC, the other to confirm the withdrawal).
That's it! After the second transaction is confirmed, the borrowed amount will show up in your crypto wallet.
Conclusion
DeFi lending and borrowing are at the forefront of innovation and can therefore be very volatile and risky. Compound and Aave both offer well-developed solutions for borrowing cryptocurrency and earning interest.
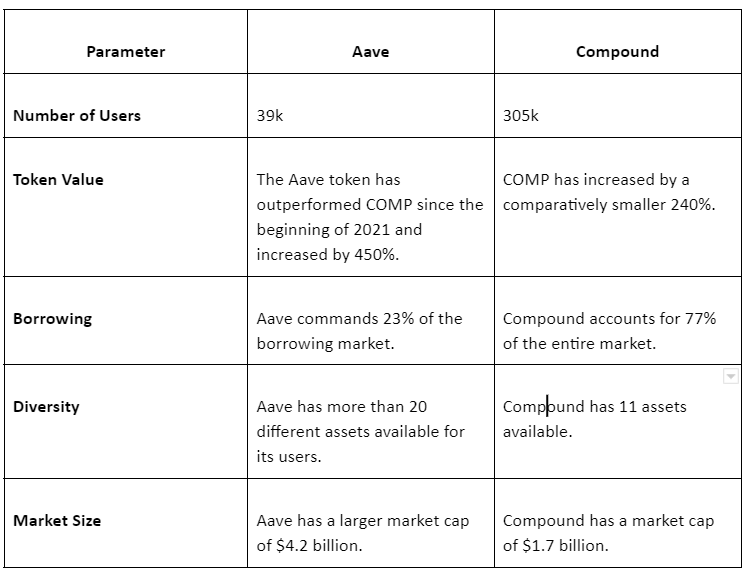
When comparing Aave and Compound, it can be argued that Aave has outperformed Compound in terms of innovation and execution. Aave offers a broader selection of cryptocurrency assets and offers unique products like flash loans.
However, Compound announced plans to create a blockchain that can offer money market and financial services across multiple networks. Unlike most DeFi exchanges that can currently only operate on the Ethereum blockchain, a Compound Chain will quickly connect to any blockchain and other networks. This move could hypothetically allow Compound to connect to digital currencies rumored to be issued by various central banks worldwide.
In the next module we will cover stablecoins and what you need to know as a beginner.



"as of April 2021"? Shouldn't it be "as of April 2022"?
Thanks for the great content :)